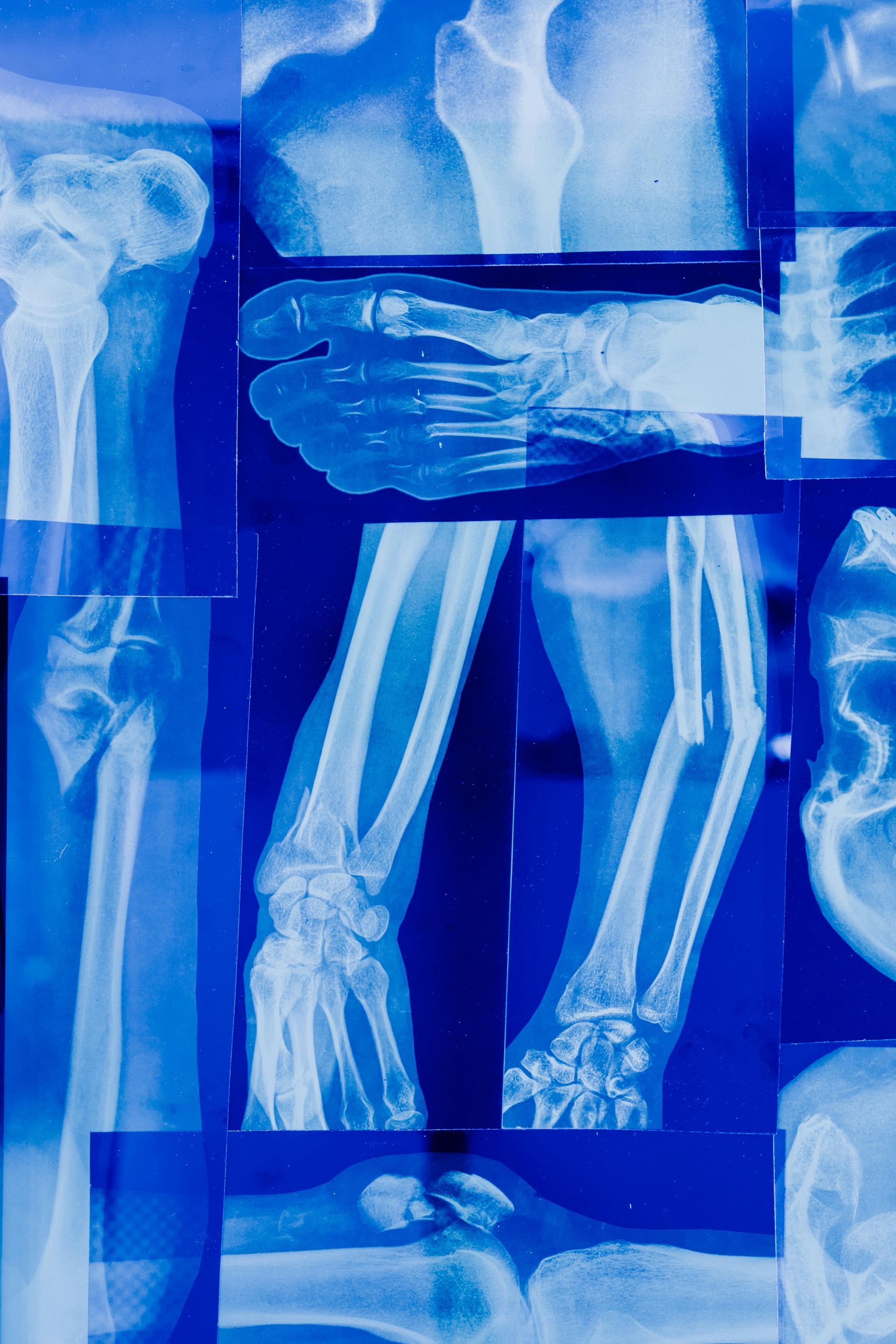
What is an MRI/CT Scan/X-Ray Showing? Understanding Your Diagnostic Imaging
At Florida Medical Orthopedic & Spine Institute, understanding your diagnostic imaging—whether it’s an MRI, CT scan, or X-ray—is crucial for effective pain management. These imaging techniques provide detailed insights into the condition of your musculoskeletal system. An MRI uses strong magnets and radio waves to visualize soft tissues, revealing issues like ligament tears or spinal injuries. A CT scan combines X-ray images for a comprehensive view, often used for complex bone fractures. Meanwhile, X-rays are invaluable for quickly assessing bone alignment and detecting fractures. By interpreting these scans, our expert physicians develop personalized treatment plans, ensuring you receive the compassionate care you deserve.
Contact Us Today
Have a question? Looking for treatment? We’re here to help. Send us a message and we’ll be in touch.
Decoding Your Doctor's Toolkit: Understanding X-Rays, CT Scans, and MRIs After an Injury
After an accident or injury, your doctor might recommend various imaging tests to get a clearer picture of what's happening inside your body. Phrases like "We're going to send you for an X-ray," or "An MRI might be necessary" can feel a bit daunting if you're unsure what these tests entail or what they can reveal.
Understanding these common diagnostic tools – X-rays, CT scans, and MRI scans – can empower you as a patient and help you better grasp your diagnosis and treatment plan. Let's break them down in simple terms.
The X-Ray: A Quick Look at Your Bones
What it is: An X-ray is often the first imaging test ordered, especially if a broken bone is suspected. It uses a small, safe amount of electromagnetic radiation to create images of the denser parts of your body, like bones.
How it works: Think of it like shining a flashlight through an object. Denser materials (like bone) block more of the X-ray beams, appearing white on the film or digital image. Softer tissues, like muscles and organs, allow more beams to pass through and appear in shades of gray or black.
What it shows in a personal injury context:
- Bone Fractures: X-rays are excellent at detecting broken bones, from hairline cracks to more significant breaks.
- Dislocations: They can clearly show if a joint is out of its normal position.
- Alignment Issues: They can help assess the general alignment of the spine or other skeletal structures.
- Foreign Objects: If an accident involved penetration, an X-ray can sometimes locate foreign objects embedded in tissue.
Limitations: X-rays provide limited detail about soft tissues like muscles, ligaments, tendons, or internal organs. If your doctor suspects an injury to these areas, they might suggest a different type of scan.
The CT Scan (Computed Tomography): A More Detailed, Cross-Sectional View
What it is: A CT scan, sometimes called a CAT scan, is a more advanced imaging technique that combines a series of X-ray images taken from different angles around your body. A computer then processes these images to create cross-sectional "slices" – think of looking at slices of a loaf of bread.
How it works: You'll typically lie on a table that slides into a large, doughnut-shaped machine. The X-ray tube rotates around you, capturing multiple images. Sometimes, a contrast dye (either ingested or injected) is used to help certain tissues or blood vessels show up more clearly.
What it shows in a personal injury context:
- Complex Bone Fractures: Provides more detail than a standard X-ray for complicated breaks or fractures in areas with many small bones (like the wrist or ankle).
- Internal Bleeding & Organ Injury: Crucial for identifying injuries to internal organs (like the spleen, liver, or kidneys) and detecting internal bleeding, especially after significant trauma like a car accident.
- Head Injuries/Brain Trauma: Can quickly detect skull fractures, bleeding in or around the brain (hemorrhage or hematoma), and some types of brain injuries. It's often used in emergency situations for rapid assessment.
- Spinal Injuries: Can show fractures of the vertebrae and issues with the spinal canal.
- Soft Tissue Damage (to some extent): Better than X-rays for visualizing some soft tissues, though MRI is often superior for detailed soft tissue assessment.
Advantages: CT scans are relatively fast and provide much more detail than standard X-rays.
The MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): The Gold Standard for Soft Tissues
What it is: An MRI uses a powerful magnetic field, radio waves, and a sophisticated computer to create highly detailed images of organs and tissues within your body. It does not use X-ray radiation.
How it works: You'll lie on a table that slides into a tube-shaped scanner. The powerful magnet causes protons in your body to align. Radio waves are then briefly pulsed, knocking these protons out of alignment. As they realign, they emit signals that are detected by the MRI scanner and processed by a computer to create detailed images.
What it shows in a personal injury context:
- Ligament and Tendon Tears: This is where MRIs truly shine. They are excellent for diagnosing injuries like rotator cuff tears, ACL tears in the knee, or Achilles tendon ruptures.
- Muscle Injuries: Can show muscle tears, contusions (bruises), and other damage.
- Spinal Cord and Nerve Injuries: Provides detailed views of the spinal cord, nerve roots, and intervertebral discs, making it invaluable for diagnosing herniated discs, spinal stenosis, or nerve compression.
- Brain Injuries: Very sensitive for detecting various brain injuries, including subtle changes that might not be visible on a CT scan, such as bruising (contusions) or diffuse axonal injury.
- Cartilage Damage: Can identify tears or damage to cartilage in joints like the knee (meniscus tears) or shoulder.
- Stress Fractures: Can sometimes detect small fractures not easily seen on X-rays.
Considerations: MRI scans take longer than X-rays or CT scans (often 30-60 minutes or more per body part). The machine can be noisy, and the enclosed space can be challenging for individuals with claustrophobia (though open MRI options are sometimes available). Patients with certain types of metal implants may not be able to have an MRI.
Your Doctor: The Key to Understanding Your Results
While it's helpful to understand what these imaging tests do, the most crucial part of the process is the discussion with your doctor. They will:
- Explain why a particular test was ordered.
- Interpret the images in the context of your specific symptoms and injury.
- Show you the images (if appropriate and helpful) and point out areas of concern.
- Discuss how the findings will influence your treatment plan.
- Answer any questions you have.
Don't hesitate to ask questions. Understanding your diagnostic imaging is a key step in understanding your injury and working with your healthcare team towards recovery.
Decoding Your Diagnosis: What Your X-Ray, CT Scan, or MRI is Telling Us
After an injury, your doctor might recommend diagnostic imaging like an X-ray, CT scan, or MRI. These tools give us a crucial window into what’s happening inside your body, helping us pinpoint the exact nature and extent of your injuries. But what do all those grayscale images mean, and what is each type of scan designed to show? Let's break down these common imaging techniques in straightforward terms.
Think of diagnostic imaging as different ways of taking pictures of the inside of your body. Each method uses different technology and excels at showing different types of structures.
X-Rays: The First Look, Especially for Bones
- How it Works: X-rays are the oldest and most frequently used form of medical imaging. They use a small, safe amount of electromagnetic radiation to create images. Dense structures like bones absorb more radiation and appear white on the X-ray film or digital image. Softer tissues, like muscles and organs, allow more radiation to pass through and appear in shades of gray or black.
- What We’re Looking For (Especially After an Injury):Bone Fractures: This is the classic use for X-rays. They are excellent at showing breaks, cracks, or chips in bones, from a hairline fracture in your wrist to a more significant break in a leg.
- Dislocations: X-rays can clearly show if a joint, like your shoulder or hip, is out of its normal position.
- Alignment Issues: After a fracture is set, X-rays help confirm the bones are aligned correctly for proper healing.
- Foreign Objects: If an accident involved debris, an X-ray might help locate foreign objects embedded in tissues (though some materials don't show up well).
- Degenerative Changes: X-rays can reveal signs of arthritis or other degenerative conditions in the bones and joints, which might be relevant to your injury or recovery.
- Advantages: Quick, widely available, and relatively inexpensive.
- Limitations: X-rays provide limited detail of soft tissues like muscles, ligaments, tendons, or internal organs. Subtle fractures can sometimes be missed.
CT Scans (Computed Tomography): Detailed Slices for a Deeper View
- How it Works: A CT scan, sometimes called a CAT scan, also uses X-rays, but it takes multiple images from different angles around your body. A computer then processes these images to create cross-sectional "slices" – imagine looking at one slice of a loaf of bread. These slices can even be reconstructed to form 3D images. You'll typically lie on a table that moves through a large, donut-shaped machine.
- What We’re Looking For (Especially After an Injury):Complex Bone Injuries: CT scans are much more detailed than X-rays for bones. They can detect subtle fractures that an X-ray might miss, show the precise alignment of fragmented bones, and are invaluable for planning surgery on complex fractures.
- Internal Organ Injuries: CT scans can help identify injuries to internal organs in the chest, abdomen, or pelvis, such as bleeding, bruising, or lacerations.
- Head Injuries/Traumatic Brain Injuries (TBI): In emergency situations, CT scans of the head are often used to quickly detect bleeding in or around the brain, skull fractures, or other acute brain injuries.
- Spinal Injuries: While MRI is often preferred for spinal cord detail, CT can be excellent for assessing fractures of the vertebrae (the bones of the spine).
- Blood Clots: In some cases, CT scans (often with a contrast dye) can help identify blood clots in vessels.
- Advantages: Provides much more detail than standard X-rays, especially for bones and some internal injuries. It's relatively fast, making it good for emergency situations.
- Limitations: Involves a higher dose of radiation than a single X-ray (though modern scanners are optimized for low doses). While better than X-rays for some soft tissues, it's generally not as detailed as an MRI for ligaments, tendons, or the spinal cord itself.
MRI Scans (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): The Gold Standard for Soft Tissues
- How it Works: Unlike X-rays and CT scans, MRI does not use ionizing radiation. Instead, it uses a powerful magnetic field, radio waves, and a sophisticated computer to create highly detailed images of organs and tissues. You'll lie on a table that slides into a tube-like scanner. The machine creates a magnetic field, and then sends radio waves through your body. These signals are picked up and converted into images.
- What We’re Looking For (Especially After an Injury):Soft Tissue Injuries: This is where MRI truly shines. It's excellent for visualizing:
- Ligament tears (e.g., ACL in the knee, rotator cuff in the shoulder)
- Tendon tears (e.g., Achilles tendon)
- Muscle tears or damage
- Spinal Cord and Nerve Injuries: MRI is the best tool for looking at the spinal cord, nerve roots, and intervertebral discs (the cushions between your vertebrae). It can show herniated discs, bulging discs, nerve compression (like sciatica), and spinal cord swelling or damage.
- Brain Injuries: MRI can detect a wider range of brain injuries than CT, including bruising (contusions), swelling (edema), and subtle changes that might indicate a concussion or more significant TBI. It's particularly good for looking at changes over time.
- Joint Problems: Detailed views of cartilage, menisci (in the knee), and other joint structures.
- Subtle Bone Injuries: While X-ray and CT are primary for bones, MRI can sometimes pick up stress fractures or bone bruising that other scans might miss.
- Advantages: No radiation exposure. Provides exceptional detail of soft tissues, nerves, the brain, and spinal cord.
- Limitations: Can be more expensive and time-consuming than X-rays or CT scans. The enclosed space can be challenging for individuals with claustrophobia (though open MRI options are available). The strong magnetic field means patients with certain types of metal implants cannot have an MRI.
Your Doctor: The Key to Understanding Your Results
While it's helpful to understand what each scan does, the most important part of the process is the discussion with your doctor. The radiologist (a doctor who specializes in interpreting these images) will analyze your scan and send a report to your personal injury doctor. Your doctor will then:
- Explain the findings in the context of your specific symptoms and injury.
- Show you the images and point out areas of concern if appropriate.
- Discuss how the results influence your diagnosis and treatment plan.
- Answer any questions you have. Don't hesitate to ask! If you don't understand a term or what a finding means for you, please speak up.
Diagnostic imaging is a powerful ally in your recovery journey. By understanding a bit more about these tools, you can feel more informed and empowered as you work with your medical team to get back on your feet.
Don't Wait, Prioritize Your Health:
The moments following an accident can be chaotic, but prioritizing your health by seeking immediate medical attention is one of the most important decisions you can make. Even if you feel seemingly unharmed, hidden injuries can be lurking beneath the surface.
If you've been involved in an accident, don't delay. Visit your nearest emergency room, urgent care, or schedule an appointment with a personal injury doctor as soon as possible. At FMOS, we are dedicated to providing comprehensive and timely care to accident victims, ensuring you receive the diagnosis, treatment, and support you need to recover fully.
Your health matters. Don't let precious hours pass without getting the medical attention you deserve.
Contact Us Today
Have a question? Looking for treatment? We’re here to help. Send us a message and we’ll be in touch.